Coupled FEM
Woo implements plate (CST+DKT) and tetrahedral (TET4) elements which are documented here and here. They use corotated FEM formulation do decompose nodal displacements into rigid-body motion and element deformation. Mass and inertia is lumped into nodes.
Horse¶
This first example shows the horse constructed from membrane elements, then from volume elements (without bones):
Tube¶
The tube is triangulated and falls (including self-collisions) onto cylinders; the material is elastic and exhibits nicely geometrical non-linearities of the deformation:
This is the same example, but rigid cylinders were replaced by deformable beam. This simulation can be found in examples/tube.py :

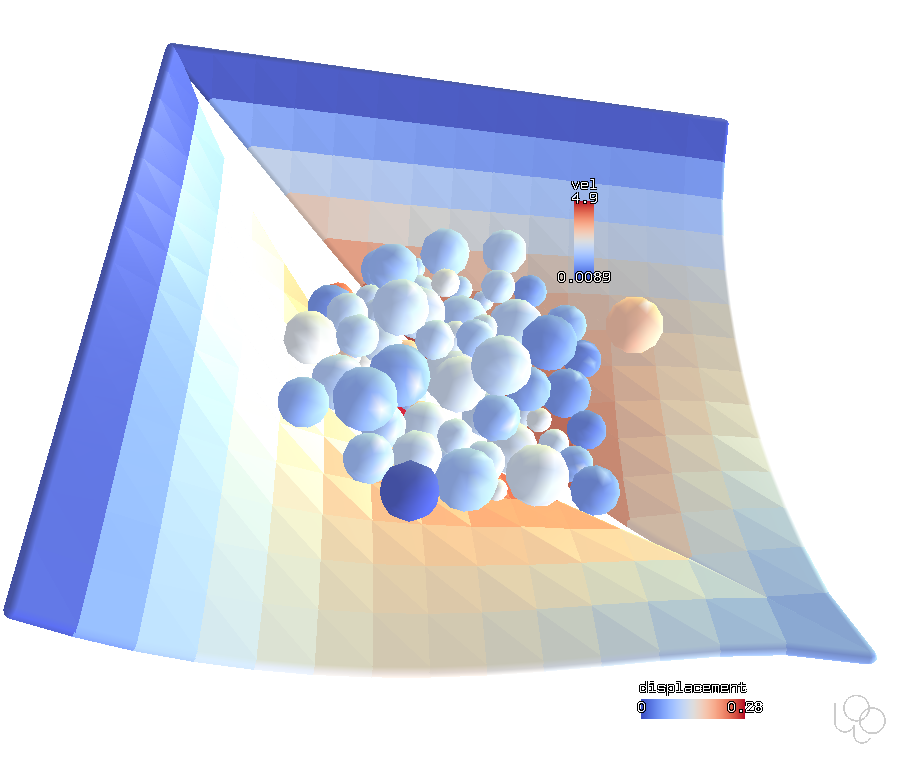
Triaxial test with membrane¶
This simulation is a preprocessor bundled with Woo; details are described in https://woodem.org/cases/cyl-triax/index.html. Triaxial test first compresses the sample isotropically, then applies hydrostatic pressure laterally (here applied by the elastic membrane) while prescribing axial deformation.
Split membrane¶
This membrane has a predefined split in the middle (used by some people to model broken plastic packaging):